What is a Qualified Retirement Plan and How do I Set One Up?
What is a Qualified Retirement Plan (QRP)? The IRS defines a QRP as one that “satisfies the Internal Revenue Code in both form and operation.” The tricky part is in that “form and operation” part. There are reams of rules and operating requirements involved. In A Guide to Common Qualified Plan Requirements, the IRS provides a list and details of 21 of the more important requirements to help employers.
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)

There are different types of individual retirement accounts, each with different goals, rules, and tax differences. For greater detail, go to IRS Publication 590-A, but here are descriptions of IRA choices:
- Traditional IRA – A Traditional IRA is a personal savings plan to set aside money for retirement. Contributions can be tax deductible. These can be individual accounts or annuities.
- Roth IRA – Roth IRAs are like Traditional IRAs, but contributions are not deductible. Instead, distributions in retirement are tax-free.
- Payroll Deduction IRA – Payroll Deduction IRAs are set up by an employer, and employees can have contributions deducted from their pay for deposit in either a Traditional IRA or Roth IRA.
- Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) – A Simplified Employee Pension or SEP is a plan set up by an employer for each employee, and the employer makes contributions directly into the plan.
- Salary Reduction Simplified Employee Pension Plan (SARSEP) – The Salary Reduction Simplified Employee Pension Plan is a type of SEP set up prior to 1997 with a salary reduction arrangement.
- Simple IRA plan – A Saving Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) is set up by the employer. Employees can contribute via salary reduction, and the employer makes matching nonelective contributions.
How Do I Open an IRA?
You can open an IRA with a variety of institutions, including:
- Banks
- Credit unions
- Life insurance companies
- Mutual funds
- Brokerages
Work with an institution that offers the type of IRA you want, and the investment options you prefer. Choose an institution what fits with how involved you want to be in selecting the investments held in your IRA.
Consider the level of online access and the online services offered as well. Especially for the hands-on business owner, the ability to access the account and work with investments online is important. You’ll typically need the following documentation to open the account:
- Appropriate identification
- Personal information, including your address, date of birth, and Social Security number.
- Beneficiary information for who inherits the account if you die.
- How you want to contribute to the account.
- Banking information for transfers.
Depending on the IRA, you could be limited to certain investments or asset classes. Almost all stocks, bonds, mutual funds, annuities, investment trusts, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real estate are permitted in IRAs. Unless you have a Self-Directed IRA, you typically can’t hold the following investment types:
- Life insurance
- Certain high-risk options
- Antiques or collectibles
- Personal use real estate
- Most coins and precious metals other than:
- American Eagle coins
- American Gold Buffalo coins (non-proof)
- American Silver Eagle
- Austrian Gold Philharmonics coins
- Canadian Maple Leaf coins
Your situation is unique, so discuss your options with a financial planner or other professional before choosing an IRA.
401(k) Retirement Plans

The 401(k) plan is a qualified retirement plan that:
- Allows an employee to elect to have their employer contribute a portion of their wages to their individual account.
- Can be profit-sharing, stock bonus, pre-ERISA money purchase pension, or a rural coop plan.
- Generally, the contributions are elective deferrals and deferred wages. They are not subject to federal income tax withholding.
- Are not reported as taxable income on the employee’s individual return.
There are three types of 401(k) plans:
- Traditional 401(k) Plans – A Traditional 401(k) plan allows eligible employees to make pre-tax elective deferrals with deductions from their payroll. Employers have the option to make contributions on behalf of all the plan participants. Employer contributions have flexible vesting rules. The plan must annually test to verify that wages deferred, and matching employer contributions do not favor highly compensated employees. The two tests are the Actual Deferral Percentage (ADP) and the Actual Contribution Percentage (ACP).
- Safe Harbor 401(k) Plans – in many ways, the Safe Harbor 401(k) is like the Traditional 401(k). The major difference is that it must provide for immediate full vesting of employer contributions. The employer can make contributions to all employee accounts or limit contributions to those who defer wages. Each year the Safe Harbor 401(k) plan must give employees written notice of their rights and obligations under the plan.
- Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) 401(k) Plan – A SIMPLE 401(k) plan is designed to help employers offer lower cost and effective retirement benefits to employees. The SIMPLE 401(k) plan is not subject to the annual ADP and ACP nondiscrimination tests. The same immediate full vesting requirement as with the Safe Harbor 401(k) plan applies to this plan. Employees in this plan may not receive contributions or benefits from any other employer plans.
Employers may avoid 401(k) plans due to the belief that they are cumbersome and expensive to set up and manage. In practice, however, there are significant benefits over those offered by the various IRA options and other plans.
Compared to Other Options, what are the Benefits of a 401(k) Plan?
Employers and employees alike can benefit from 401(k) plans. The plan helps employers attract and retain talented employees. Other benefits include:
- Employer matching – Employers have two ways to match contributions for employees:
- The employer can match a percentage of employees’ contributions as a stated portion of their total salary.
- The employer can match up to a stated dollar amount independent of the salary of the employee.
- Tax advantages – employees are saving for retirement with pre-tax dollars. They pay no taxes on the amounts they contribute to their accounts. Instead, when they retire, they will pay taxes on withdrawals.
- Startup cost tax credits – Based on employer eligibility, an employer may have an opportunity to claim a tax credit of up to $5,000 for the first three years to pay for costs involved in starting a qualified 401(k) plan.
Many employers prefer a 401(k) plan due to the long term benefits.
How Do I Set Up a 401(k) Plan?
Before setting up a plan, do your research and understand the different choices in the context of your business operations. Once you have gathered information to make an informed decision, you should work with a retirement services provider. Many reputable companies can help with retirement plans, but here’s a short list from NerdWallet to help compare features and fees 7 Top 401(k) Providers for 2022:
- ADP
- Betterment for Business
- Charles Schwab
- Sharebuilder 401(k)
- Fidelity Investments
- T. Rowe Price
- Merrill Edge
Considerations for Choosing a 401(k) Services Provider
Five considerations for choosing where to set up your 401(k) Plan:
- They offer the plan type and options that you want. Not all providers are the same, and there are choices as to employee eligibility, vesting, investments, and other details. You want to be sure that your chosen provider offers the plan and options that meet your needs.
- There are fees involved in managing your plan, so get a clear picture of the fees involved in having your plan services right for your business and employees.
- Customer service is important, especially for the busy business owner who may have questions or decisions that require consulting with their 401(k) service provider. Be sure that you can get the help you need when you need it.
- Consider a provider that will act as a fiduciary advisor. A fiduciary is legally bound to act in the best interests of their client and provide unbiased advice.
- In today’s world, the availability of online access to manage or monitor accounts is a plus. You may want to check account investment performance or other information during non-business hours as well.
Take the time you need to evaluate different plans and service providers.
Help With Choosing a Retirement Solution for Your Business
This IRS publication Choosing a Retirement Solution for your Small Business will help you quickly compare key advantages, eligibility, and limitations for each retirement account type.
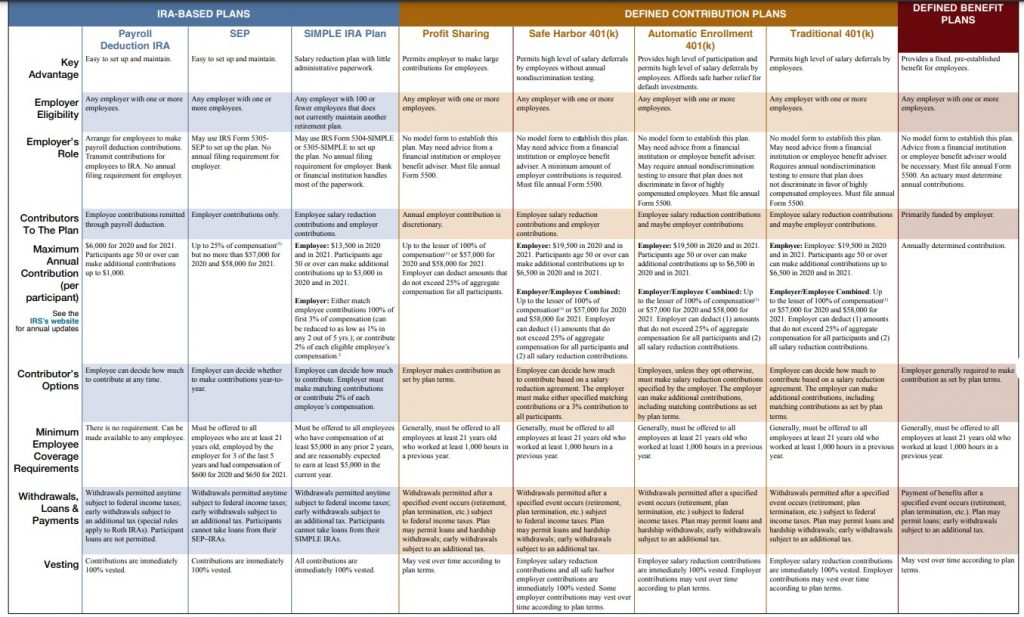
The publication also provides other IRS Publication resources with more detail about different retirement plans.
Summary
It’s never too early to start saving for retirement. Start early to take advantage of compounding interest. In today’s business world, it’s challenging than ever to attract and retain talented employees. The right retirement plan can be a powerful recruiting tool and a competitive advantage.

